Your shopping cart is empty!
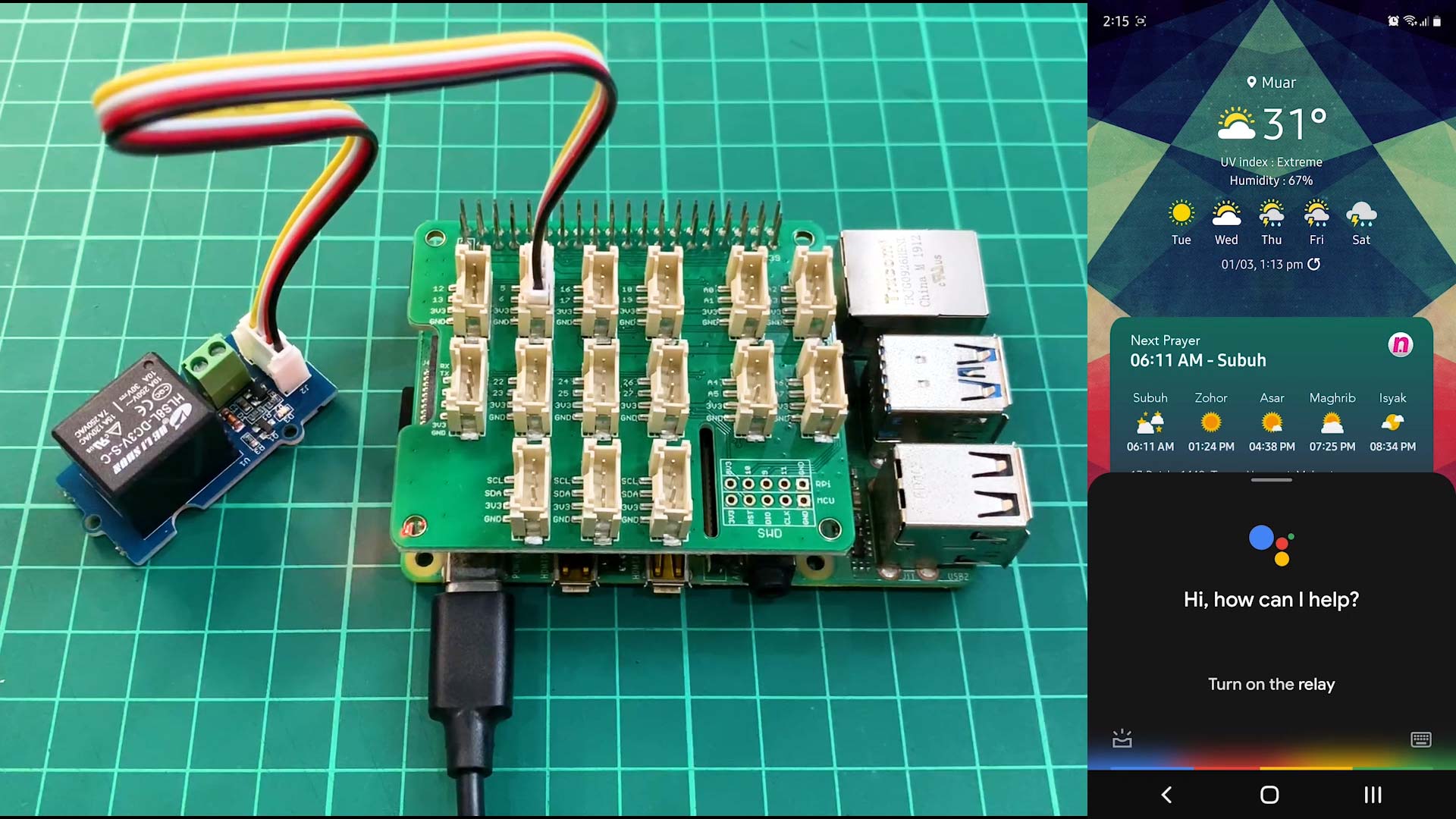
Google Assistant Controlled Raspberry Pi GPIO With IFTTT and Adafruit IO
- Idris Zainal Abidin
- 03 Mar 2021
- 640
Introduction
We have shared a tutorial of Google Assistant and Raspberry Pi last year using IFTTT and Particle IO. But Particle IO no longer supports the Raspberry Pi, so the previous tutorial is obsolete. For this tutorial, we will try to update using IFTTT and Adafruit IO platforms.
Video
This video shows how to control relay using Raspberry Pi and Adafruit IO.
This video shows how to link between Google Assistant and Adafruit IO using IFTTT.
Hardware Preparation
This is the list of items used in the video.
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (2GB)
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (4GB)
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (8GB)
- Phidisk Class10 MicroSD
- Official RPi USB-C Adapter
- Grove Base Kit for Raspberry Pi
Sample Program
This is python3 sample program to control relay module connected to Raspberry Pi using Adafruit IO. Please install following libraries:
sudo pip3 install adafruit-blinka sudo pip3 install adafruit-io
Thank You
References:
Thanks for reading this tutorial. If you have any technical inquiries, please post at Cytron Technical Forum.
"Please be reminded, this tutorial is prepared for you to try and learn.
You are encouraged to improve the code for a better application."
 International
International Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam