Your shopping cart is empty!
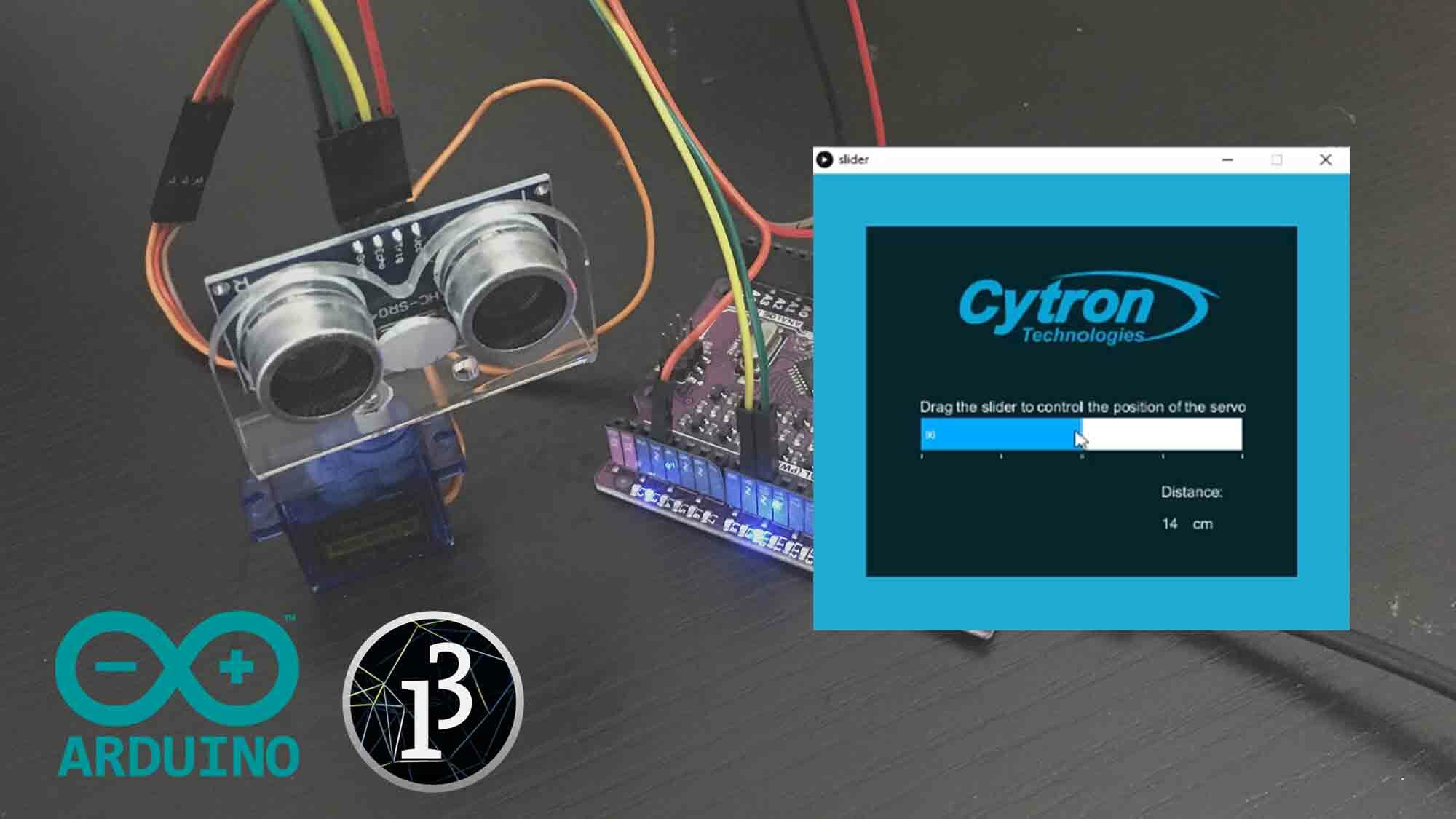
Control A Servo And Display Sensor’s Reading Using The GUI On Arduino.
Introduction
Arduino can also be controlled by the Graphical User Interface (GUI). We create the GUI using Processing IDE. It's quite easy to create the GUI. In this tutorial, we will create a simple GUI to control the Servo and display sensor's reading on Arduino. The sensor can be any sensor, but in this tutorial we're using Ultrasonic sensor.
Video
This video will show you how to create a user interface that can control a servo and display sensor's reading on Arduino with Processing.
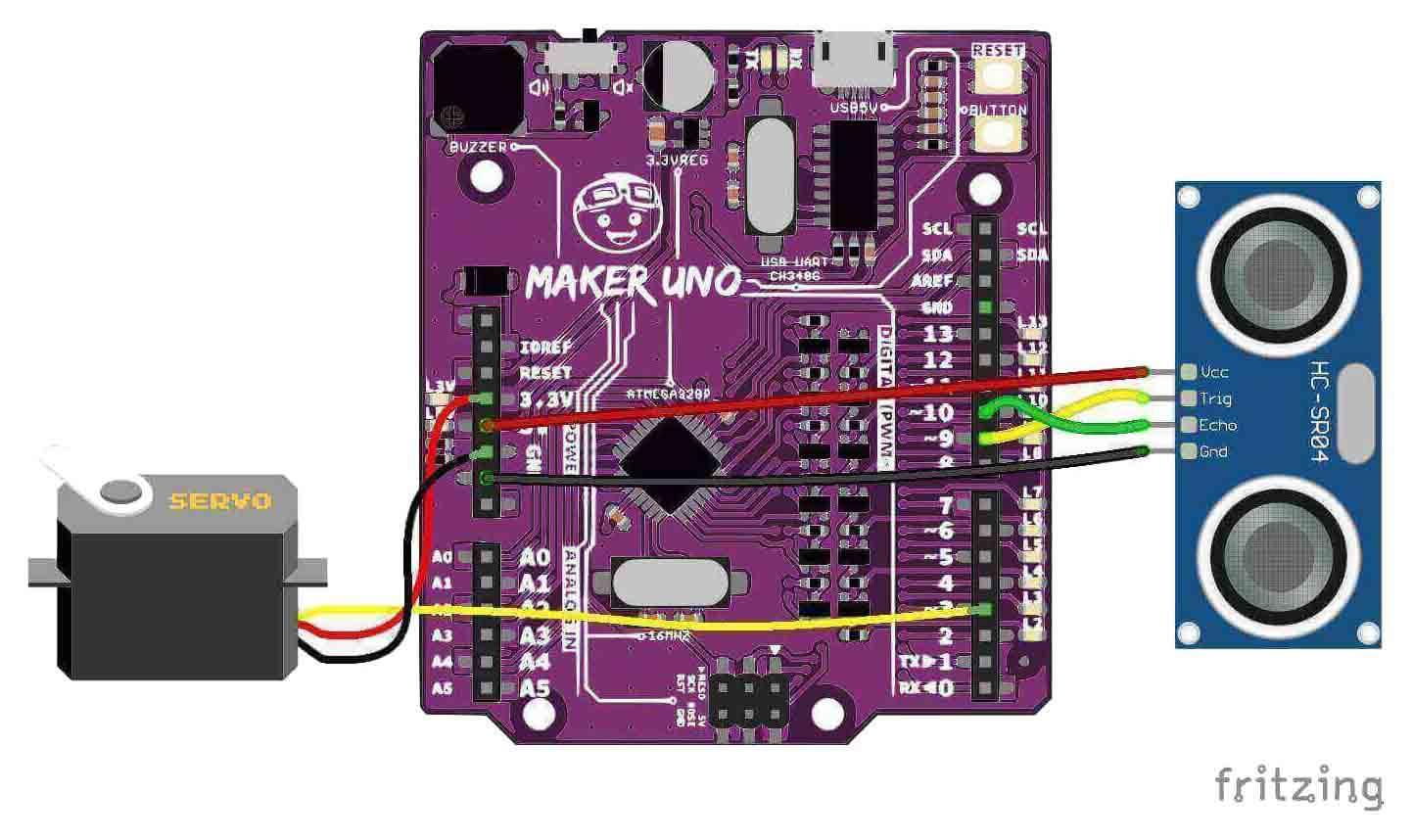
Hardware Preparation
This is the hardware connection and the components needed.
Sample Code
Arduino
Processing
References :
Thank you
Thank you for reading this tutorial and we hope it helps your project development. If you have any technical inquiry, please post at Cytron Technical Forum.
 International
International Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam