Your shopping cart is empty!
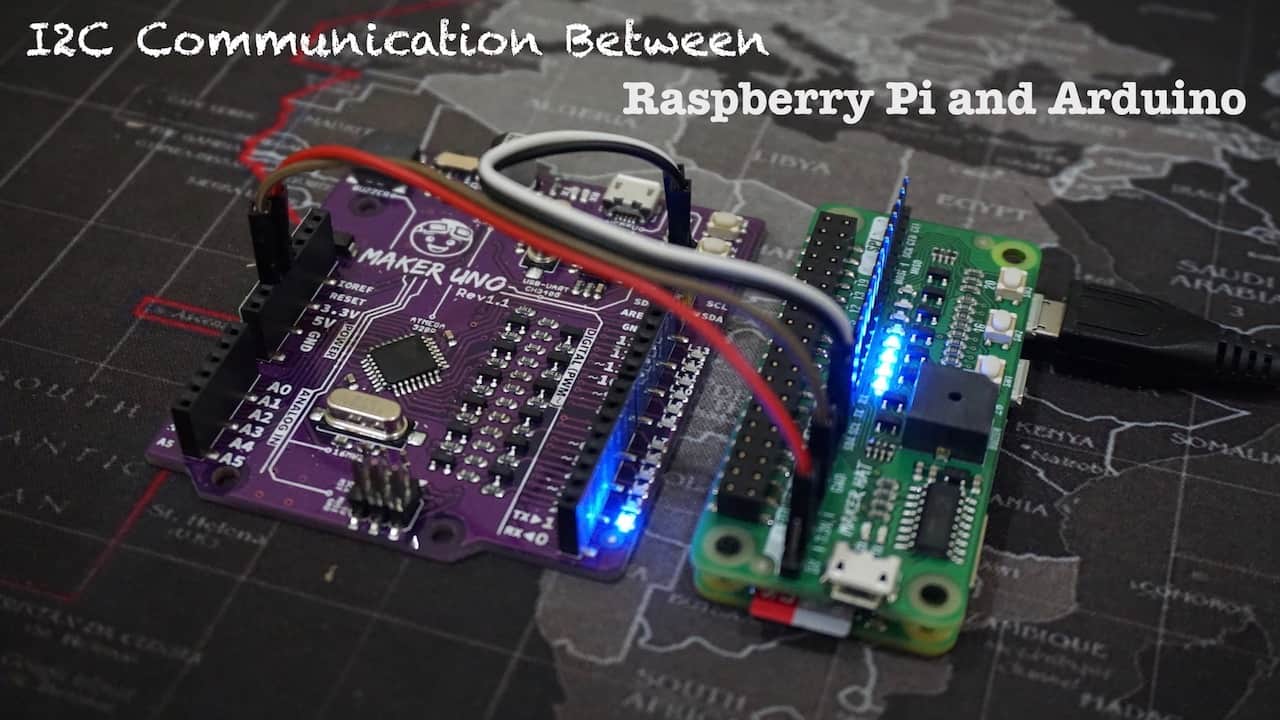
I2C Communication Between Raspberry Pi and Arduino
- Idris Zainal Abidin
- 25 Sep 2018
- 499
INTRODUCTION
Besides controlling I2C modules, like display and sensors, I2C communication also can be implemented between 2 controllers. For example between Raspberry Pi and Arduino. The different compare to I2C module is, we need to create our own data protocol. So this tutorial will show you how to communicate between Raspberry Pi and Arduino Using I2C.
You may need to refer following tutorial first:
VIDEO
This video will show you how to communicate between Rasapberry Pi and Arduino Using I2C.
ITEM USED IN THE VIDEO
Sample Code
This is the sample code for Arduino and Raspberry Pi used in the video.
Thank You
References
- Controlling an Arduino from a Pi3 using I2C
- i2c python documentation
- Raspberry Pi SPI and I2C Tutorial
- Master Writer/Slave Receiver
Thanks for reading this tutorial. If you have any technical inquiry, please post at Cytron Technical Forum.
Related Products
Maker UNO: Simplifying Arduino for {Education}
$9.00 $9.00
x 1 unit(s)
Maker pHAT: Simplifying Raspberry Pi for {Educa...
$10.90 $10.90
x 1 unit(s)
 International
International Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam